

Innovation in the construction of steelwork structures is endemic, driven by continual striving for cost-effective, time-efficient and risk-minimised solutions in a nationally and internationally competitive market. Every steel structure is ultimately a bespoke design, responding to external environmental influences and complex user requirements. Therefore, every solution has the opportunity for innovation to provide differentiation in a crowded marketplace.
Below are just some of the areas in which innovation has been put into practice recently. You can also head over to the ASI Innovation Portal to view first-hand the innovation underway in our research institutions.
CAD/CAM: Computer-aided design (CAD) and computer-aided manufacture (CAM) have revolutionised the process of converting ideas into real-world structures, no more so than in the structural steel space
BIM: Building information modelling is a process involving the generation and management of digital representations of physical and functional characteristics of places. Its adoption is becoming increasingly entrenched in this country
3D laser scanning: a 3D laser scanner analyses 3D objects and returns information about the object, usually to enable the geometric shape to be calculated, but also possibly its appearance
AR/VR: Augmented reality (AR) and Virtual reality (VR) have moved from gaming environments to providing solutions that are natural adjuncts to working on fundamentally 3D structures.
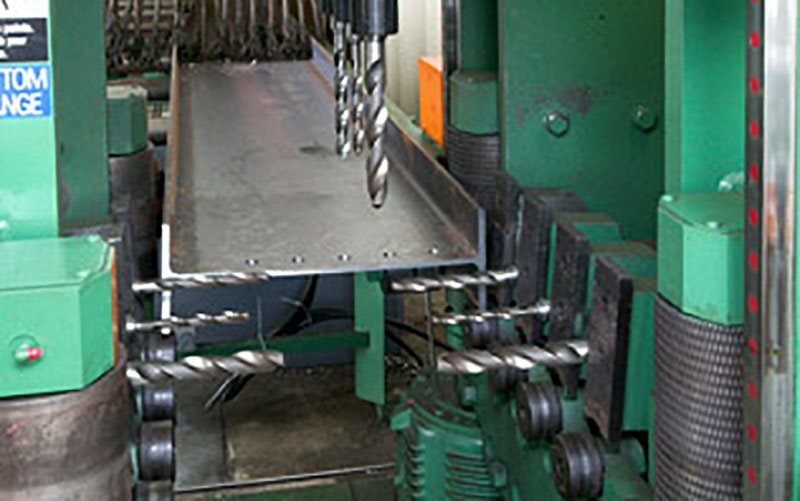
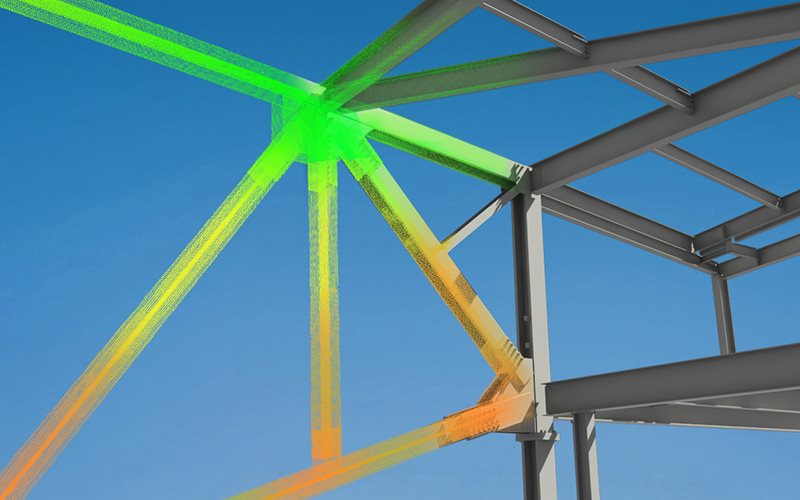

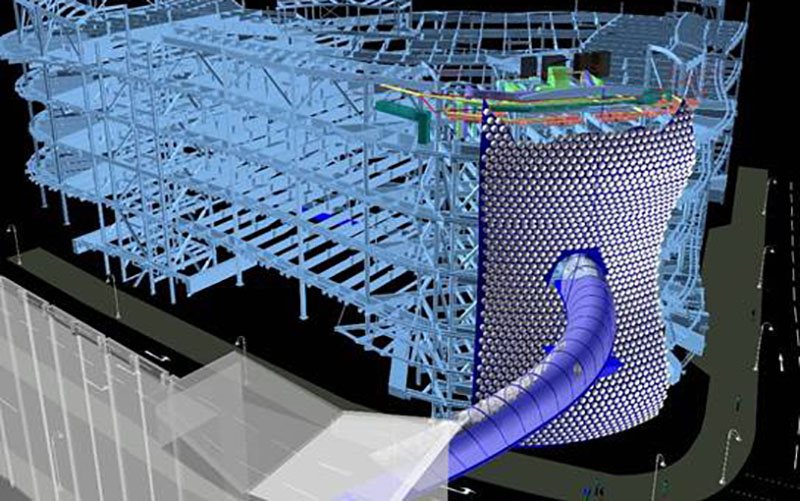

(L to R) CAD/CAM / Building Information Modelling (BIM) / 3D laser scanning (Courtesy PDC).
Augmented reality welding simulation: recent AR/VR developments in welding simulators that superimpose simulated welding onto real-world steel connections provide a cost-effective and environmentally friendly approach to initial welder training.
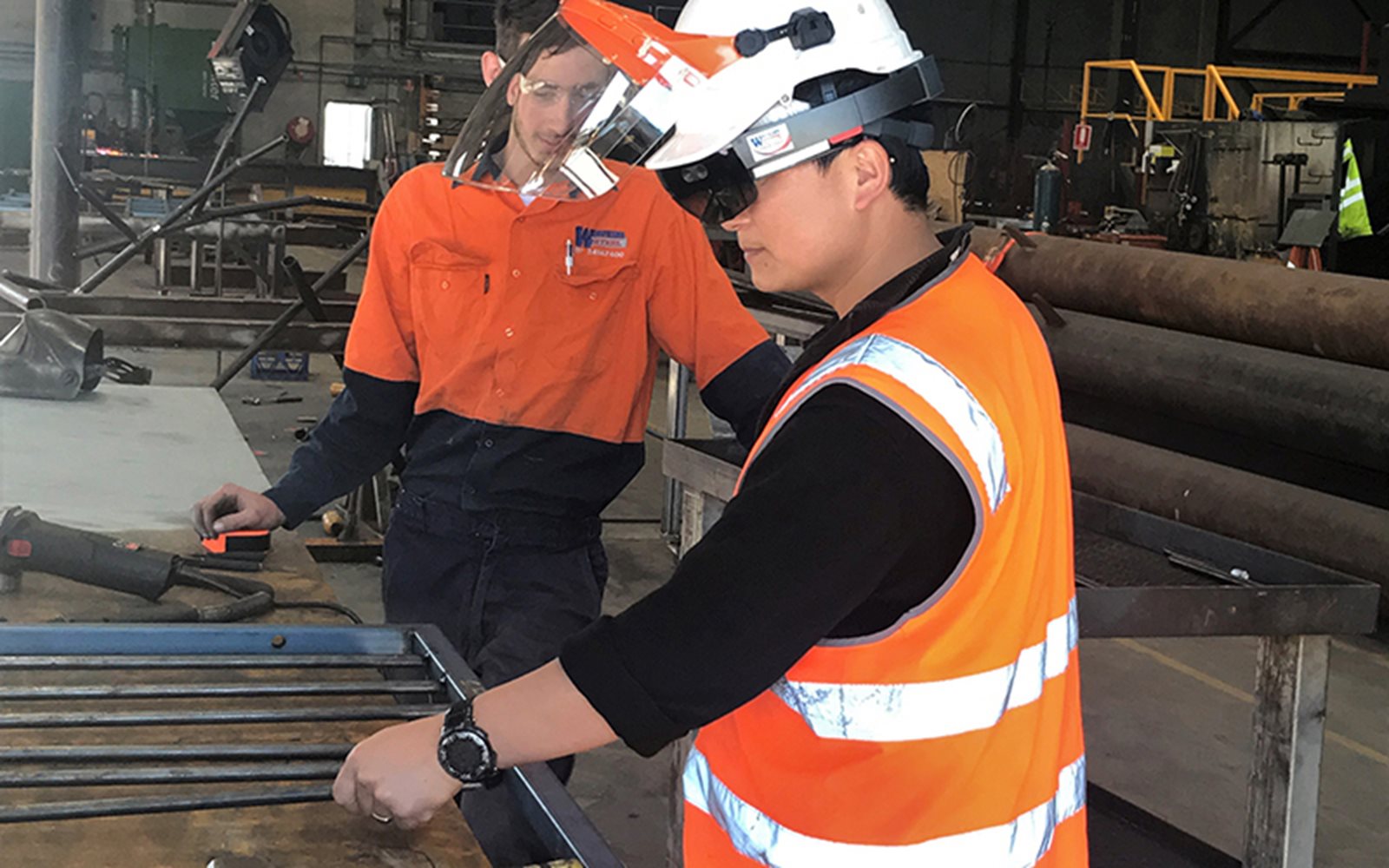
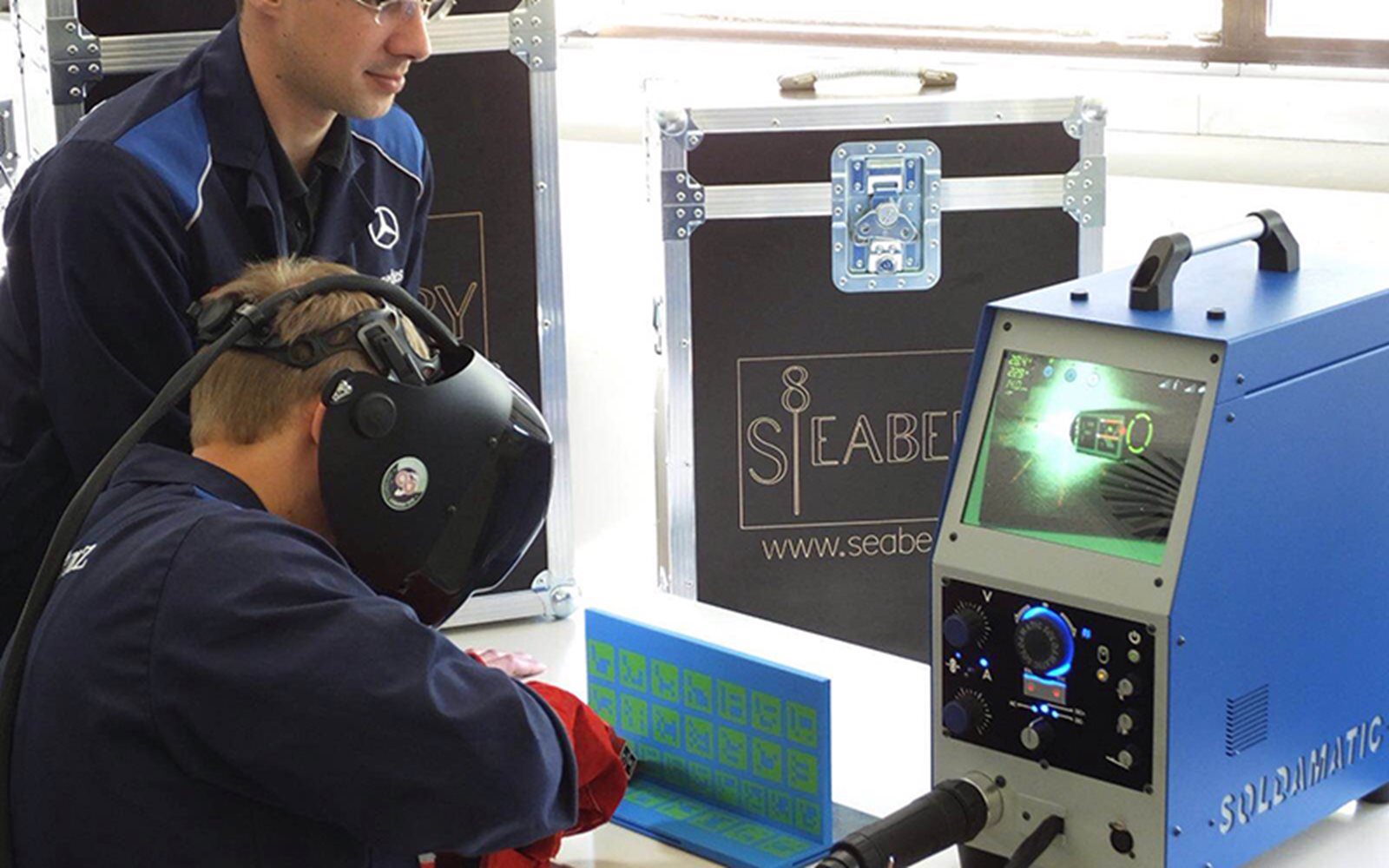
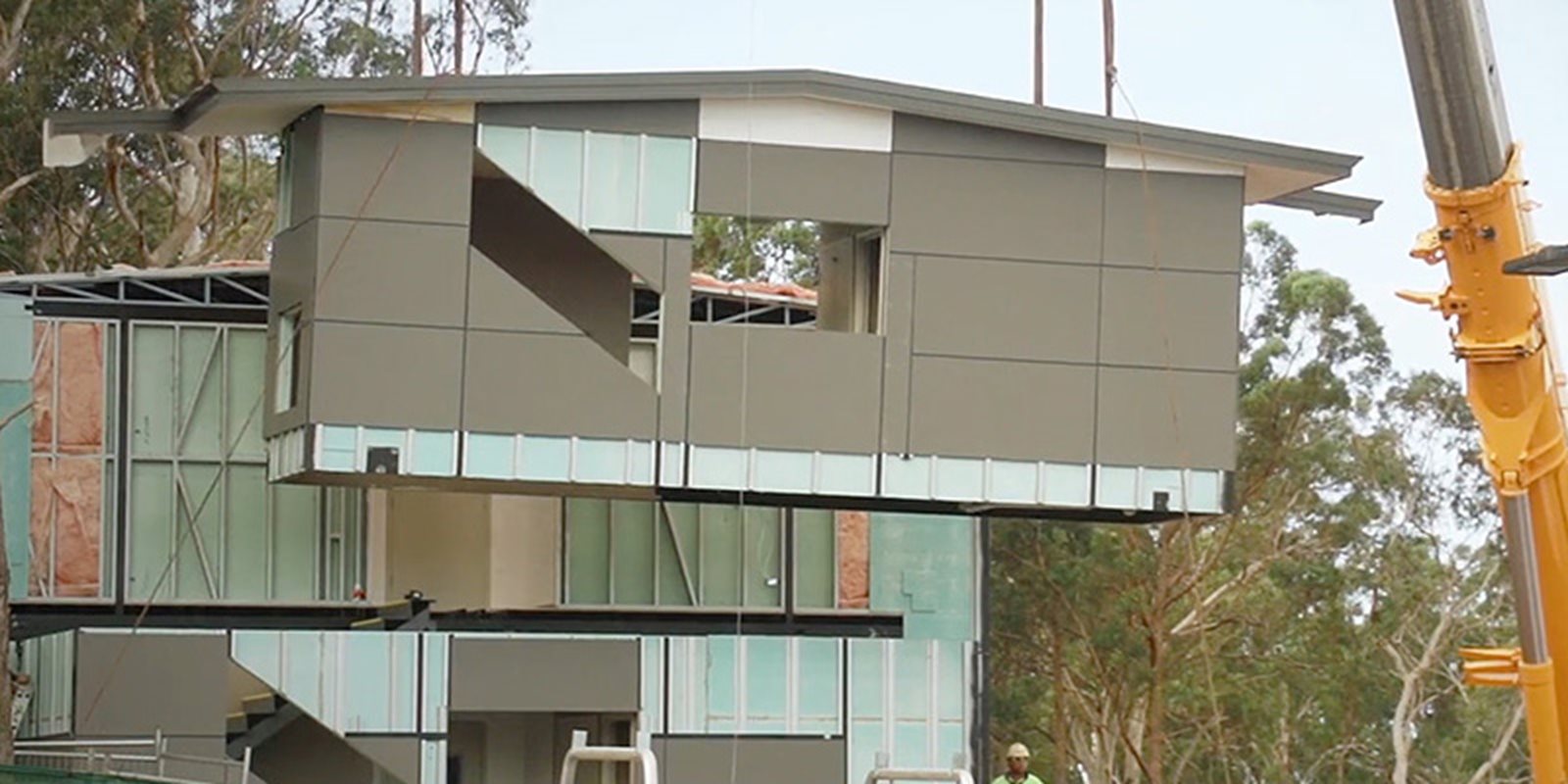



(L to R) AR/VR (Courtesy Watkins Steel) / Augmented reality welding simulation (Courtesy Weld Australia) / Modular construction (Courtesy Intelligent Building Systems International).
Modular construction: modular construction can be described as any form of construction where some form of prefabricated component or module is brought to site pre-assembled and erected into the final structural form
High-strength steel: high-strength quenched and tempered steels offer the design engineer a number of advantages that can be exploited in developing solutions to both every day and difficult or unusual engineering problems
3D printing of steel: 3D printing of metallic components is in its infancy, but sure to put the industry under disruptive pressures
Steel building core systems: replacing the traditional concrete building core systems with composite steel-concrete solutions for increased stiffness and speed of construction.
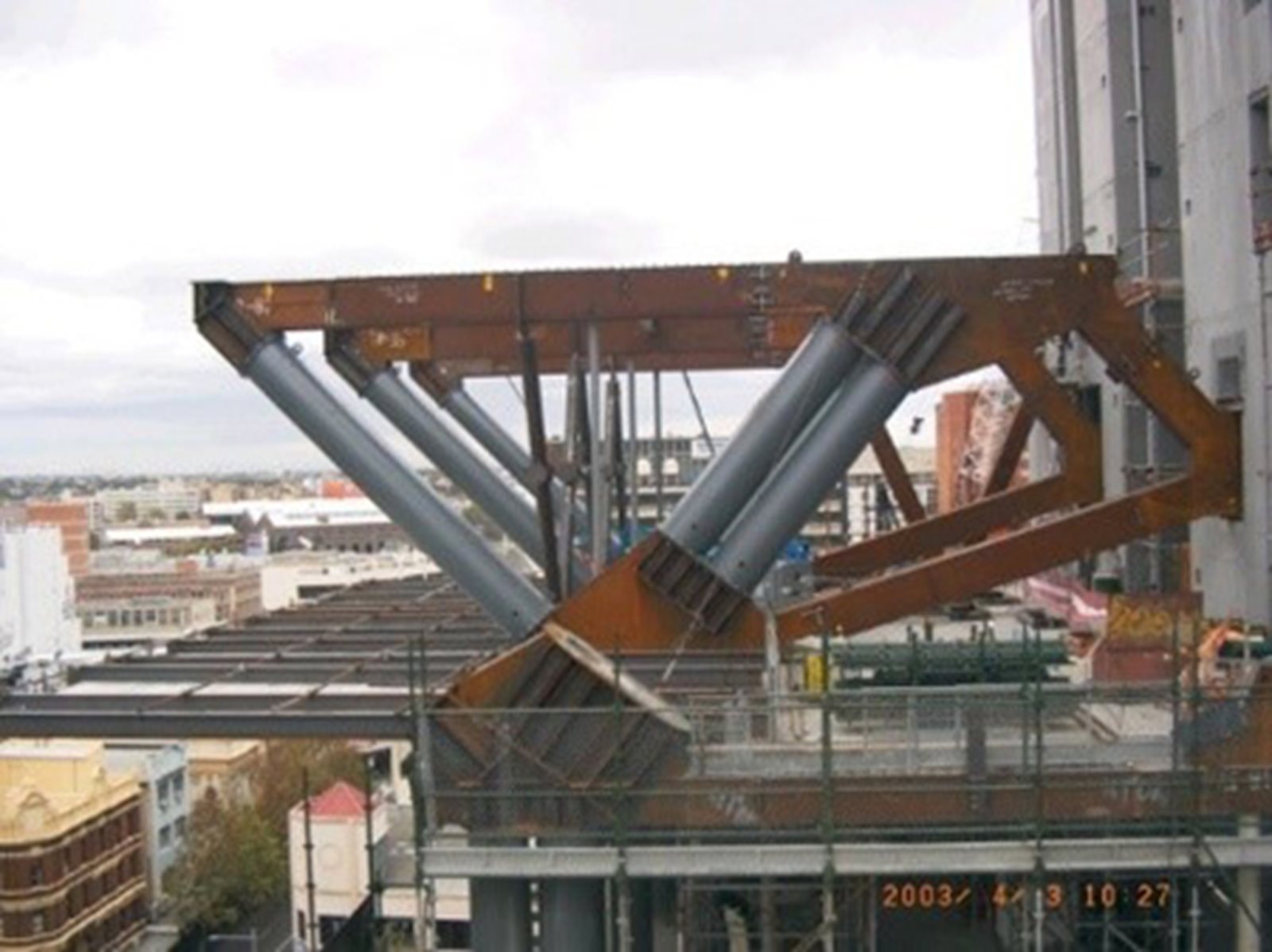
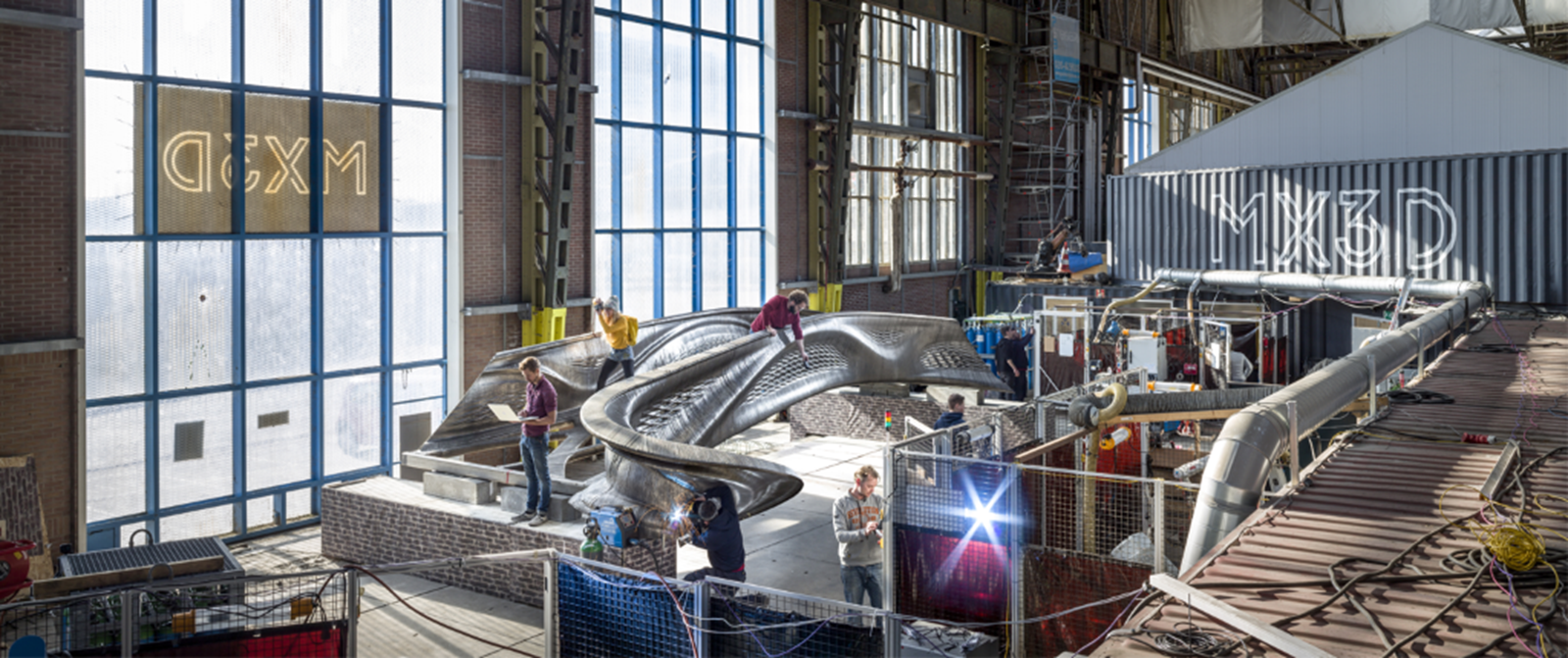
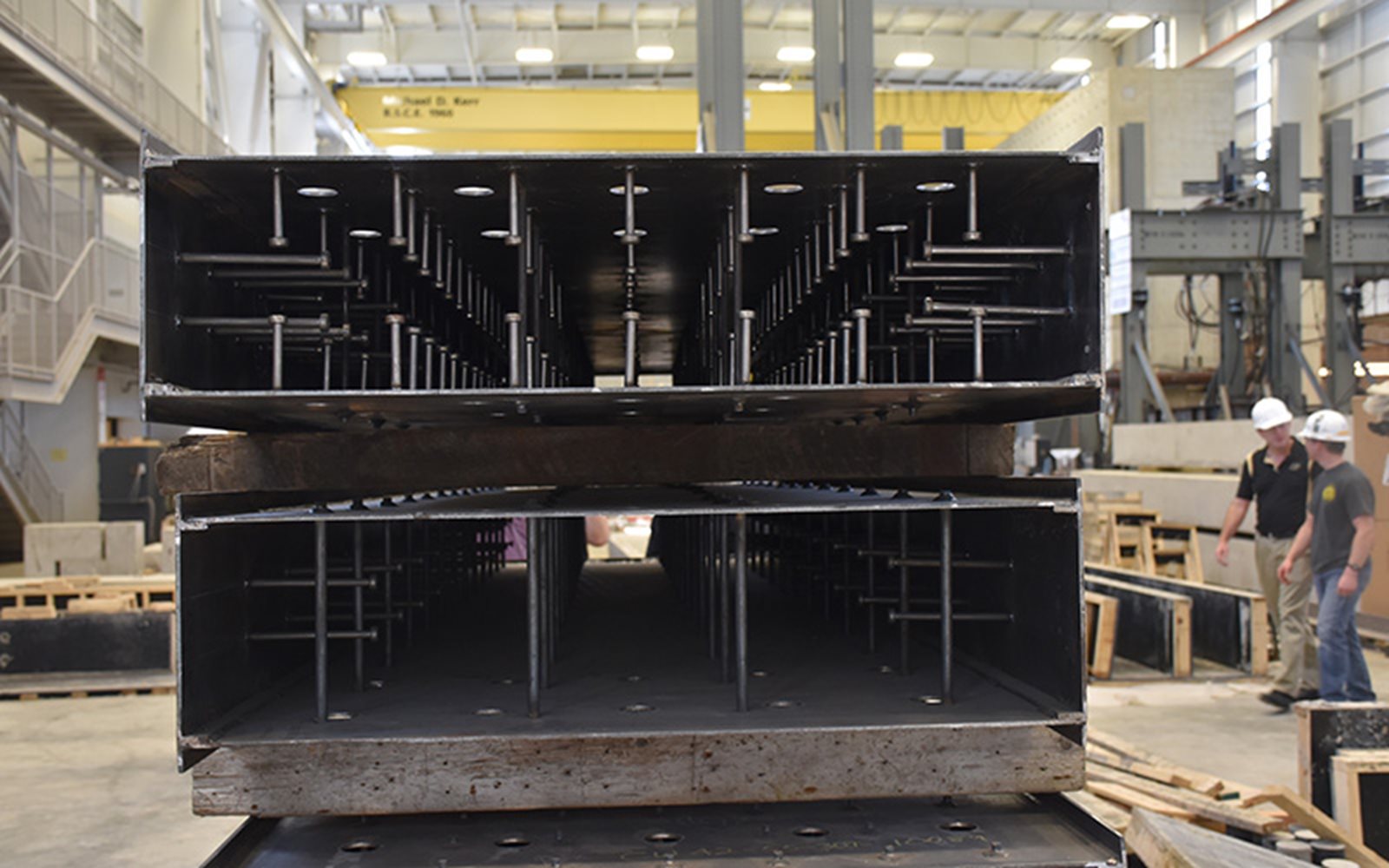



(L to R) High-strength steel (Courtesy Alfasi Steel) / 3D printing of steel (Courtesy MX3D) / Steel building core systems (Courtesy AISC).